Adenovirus infection
OVERVIEW
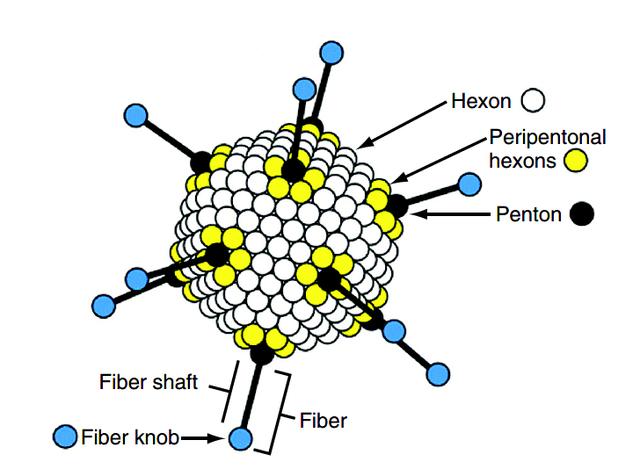
What does adenovirus look like?
Adenovirus is a non-enveloped, double-stranded linear DNA virus with over 70 serotypes and relatively low variability[1].
Infection with adenovirus can cause diseases in various systems, most commonly respiratory infections such as rhinitis and pneumonia. Additionally, adenovirus infection may lead to keratoconjunctivitis and pediatric gastroenteritis. In severe cases, it can also cause hepatitis, nephritis, myocarditis, and meningitis[1,2].
Is adenovirus infection common?
Yes. Adenovirus infections occur worldwide and can happen in any season, with winter and spring being peak periods. People of all ages are susceptible, but children are more commonly infected due to their underdeveloped immune systems. Studies show that respiratory adenovirus infections account for 5%–10% of global pediatric respiratory infections, meaning 5–10 out of every 100 children with respiratory infections are infected with adenovirus[3].
How is adenovirus transmitted?
Adenovirus is contagious and spreads primarily through droplets, contact, and fecal-oral routes.
The main mode of transmission is droplet spread. Both infected individuals and asymptomatic carriers (who show no symptoms but are contagious) shed large amounts of adenovirus in respiratory secretions. Talking, coughing, or sneezing releases droplets into the air, which others may inhale and become infected[4].
Adenovirus can also spread through contact (mouth, nose, eyes), fecal-oral transmission, or contaminated objects. Therefore, handwashing before eating is essential, and actions like rubbing eyes or picking the nose should be avoided. Wearing masks when going out is recommended[4].
What happens after adenovirus infection?
Adenovirus is contagious, but some infected individuals may show no symptoms. The infection is also self-limiting, so many people may not realize they are infected.
However, if symptoms such as cough, nasal congestion, sore throat, accompanied by fever, chills, or headache occur, medical attention should be sought promptly. Infants, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals may experience prolonged illness, which can severely impact their health[1].
SYMPTOMS
Which organs are affected by adenovirus?
Different types of adenoviruses affect different organs. Refer to the table below for details:
| Adenovirus Classification | Phenotypes | Affected Organs or Systems |
|---|---|---|
| A | 12, 18, 31 | Primarily digestive tract, occasionally respiratory tract |
| B | 3, 7, 11, 14, 16, 21, 34, 35, 50, 55 | Respiratory tract, genitourinary tract |
| C | 1, 2, 5, 6, 57 | Respiratory tract, liver |
| D | 8, 10, 13, 15, 17, 19, 20, 22, 30, 32, 33, 36-39, 42-49, 51, 53, 54, 56, 58-60 | Eyes, digestive tract |
| E | 4 | Respiratory tract |
| F | 40, 41 | Digestive tract |
| G | 52 | Digestive tract |
Overall, adenoviruses most commonly affect the respiratory tract, eyes, digestive tract, and genitourinary system[1,5].
What are the symptoms of adenovirus infection?
Adenovirus infection typically has an incubation period of 5–12 days and can persist for weeks or even months. Symptoms vary depending on the infection site:
- Respiratory tract infection: Cough, nasal congestion, sore throat, accompanied by fever, chills, and headache. Severe cases may develop pneumonia, presenting as persistent high fever (above 38.5°C), shortness of breath, and chest tightness. Critical cases may lead to shock, respiratory failure, or death. Adenovirus pneumonia is particularly dangerous for children[2].
- Eye infection: Keratoconjunctivitis, causing eye redness, foreign body sensation, tearing, and photophobia.
- Digestive tract infection: Abdominal pain and diarrhea. In children, severe conditions like intussusception may occur, presenting as severe abdominal pain, vomiting, abdominal mass, and currant jelly stool.
- Urinary tract infection: Frequent, urgent, and painful urination.
- Vaginal infection: Vaginitis or cervicitis, causing abnormal discharge and itching[6-8].
Can adenovirus infection cause serious diseases?
- While adenovirus infections are usually self-limiting, they can lead to prolonged illness or complications.
- Infants and young children are at higher risk of severe outcomes, such as viral pneumonia, which is difficult to treat. Group C adenoviruses may cause intussusception in children, sometimes requiring surgery.
- In adults, adenovirus can cause severe hepatitis, nephritis, myocarditis, or meningitis, requiring prompt treatment[6-8].
Can adenovirus cause cancer?
Some studies suggest that certain adenoviruses (e.g., type A12) can induce tumors in animals, but no evidence confirms this in humans[1,4].
Do different adenovirus types cause the same symptoms?
No. Different adenovirus types target different organs, leading to varied symptoms:
- Group C adenoviruses can cause acute febrile pharyngitis or intussusception in children.
- Group B adenoviruses may lead to swimming pool conjunctivitis or viral pneumonia.
For example, serotypes 40 and 41 typically cause gastroenteritis in children under 4, while serotype 37 can cause cervicitis in women and urethritis in men. Serotypes 11 and 12 are linked to acute hemorrhagic cystitis in children[6-8].
What respiratory symptoms does adenovirus cause?
Adenoviruses account for 5% of pediatric upper respiratory infections and 10% of childhood pneumonia. Upper respiratory infections mainly present as pharyngitis, rhinitis, or tracheitis (not bronchitis), often with fever, malaise, headache, myalgia, and abdominal pain. In fact, adenovirus is the most common cause of tonsillitis in young children.
Infants may also develop otitis media. Adenovirus-related tonsillitis can mimic whooping cough. Some serotypes cause severe pneumonia, increasing mortality risk.
In adults, symptoms may start as a cold, progressing to bronchitis or pneumonia, lasting 5–7 days (up to 2 weeks). Secondary bacterial infections can occur[6-8].
How does adenovirus affect the eyes?
Conjunctivitis often accompanies pharyngitis and cervical lymphadenitis. Some cases progress to painful keratoconjunctivitis, causing corneal opacity and blurred vision. Eye pain can be severe, lasting up to 4 weeks, but permanent corneal damage is rare[6-8].
What gastrointestinal symptoms does adenovirus cause?
In children, adenovirus serotypes 40 and 41 (Group F) cause 5%–10% of acute diarrheal illnesses. Diarrhea lasts 8–12 days on average, often with fever and vomiting.
Other adenovirus types may cause mesenteric lymphadenitis (mimicking appendicitis) or intussusception[6-8].
CAUSES
What are the causes of adenovirus infection?
-
The main cause of adenovirus infection is close conversation or contact with infected individuals or asymptomatic carriers, leading to exposure to the virus. When adenovirus invades the respiratory tract, digestive tract, or urinary tract, it manifests as a series of symptoms, resulting in adenovirus infection.
-
Additionally, adenovirus infection is closely related to the body's immune system. Individuals with weakened immunity, such as children whose immune systems are not fully developed, are more susceptible. Therefore, while avoiding or minimizing exposure to adenovirus, it is important to exercise and boost immunity[6-8].
Which groups are at higher risk of adenovirus infection?
People of all ages can be infected with adenovirus.
Adenovirus infections often occur in crowded settings such as schools and military camps. Due to factors like incomplete immune function in young children and intense training among new recruits, students and military trainees are more prone to group infections[1,4].
Moreover, adenovirus infection is more common and can have severe consequences in individuals with hematopoietic stem cell transplants, solid organ transplants, congenital immunodeficiency, or acquired immunodeficiency.
DIAGNOSIS
Can adenovirus infection be self-diagnosed?
Adenovirus infection cannot be self-diagnosed because the diseases it causes often resemble those caused by other pathogens, including pneumonia, pharyngitis, gastroenteritis, hepatitis, and urinary tract infections. Without etiological testing, the pathogen cannot be accurately identified.
Moreover, adenovirus infections are usually difficult to cure, and there are no effective specific drugs. Conventional or bacterial infection treatments may not yield improvement, so self-diagnosis should be avoided to prevent delays in treatment[7-9].
How is adenovirus infection diagnosed?
Generally, a preliminary diagnosis can be made based on the patient's symptoms, close contact history with confirmed cases, and a positive result for adenovirus-specific nucleic acid testing.
- Patients with pharyngitis or pneumonia may have adenovirus nucleic acid detected in sputum or throat swabs;
- Patients with gastroenteritis may have adenovirus nucleic acid detected in stool;
- Patients with conjunctivitis may have adenovirus nucleic acid detected in eye secretions;
- Patients with urinary tract infections may have adenovirus nucleic acid detected in urine;
- Patients with vaginitis may have adenovirus nucleic acid detected in vaginal discharge or secretions[2,7,9].
In addition to nucleic acid testing, clinical diagnosis may also include adenovirus-specific antigen testing, viral culture, and virus isolation.
What other tests are needed for adenovirus infection?
Besides etiological testing, doctors may also order the following tests:
- Complete blood count and biochemistry: To assess the severity of infection and evaluate liver and kidney function.
- Urinalysis: To check for hematuria and determine if the genitourinary system is affected.
- Imaging tests: Mainly X-rays or CT scans to further evaluate lung infections.
- Colonoscopy: To assess intestinal infections.
Which diseases resemble adenovirus infection? How are they distinguished?
- Differentiating adenovirus lung infection from other viral lung infections: Other viruses, such as respiratory syncytial virus, influenza virus, and parainfluenza virus, are also contagious and can cause symptoms like cough, fever, and chills, potentially leading to pneumonia. Etiological testing is necessary for definitive differentiation.
- Differentiating adenovirus gastrointestinal infection from acute gastroenteritis: Both cause abdominal pain and diarrhea, but acute gastroenteritis typically occurs after consuming contaminated food, with more severe pain, and adenovirus is not detected in stool tests.
- Differentiating adenovirus eye infection from bacterial or fungal eye infections: Both cause eye swelling and pain, but adenovirus infection is usually confined to the conjunctiva, with large amounts of adenovirus detectable in eye secretions.
- Differentiating adenovirus urinary tract infection from E. coli urinary tract infection: Both cause urinary urgency and pain, but adenovirus infection often presents as hemorrhagic cystitis, which usually resolves on its own. Severe E. coli infections may also cause fever, fatigue, and loss of appetite[7-9]. Etiological testing can distinguish between them.
TREATMENT
Which department should I visit for adenovirus infection?
The choice of department for adenovirus infection should be based on clinical manifestations, or you can directly choose the infectious disease department.
- If symptoms such as cough and chest tightness appear, you should visit the respiratory department;
- For digestive symptoms like abdominal pain or diarrhea, go to the gastroenterology department;
- For conjunctivitis, visit the ophthalmology department, and for vaginal infections, see the gynecology department;
- Urinary tract infections should be treated in the urology department[6-8].
Can adenovirus infection heal on its own?
Most adenovirus infections can resolve on their own. If symptoms are mild or detected incidentally without clinical manifestations, medical attention may not be necessary, as the condition often heals spontaneously.
However, if symptoms are severe, such as persistent cough, chills, fever, abdominal pain, or diarrhea, prompt medical treatment is recommended to avoid complications[7,8].
Is adenovirus infection easy to treat?
Adenovirus infection is not easy to treat because there is currently no specific antiviral medication. Treatment focuses on symptom relief and boosting the patient's immunity to fight the virus[4].
How is adenovirus infection treated?
-
Respiratory support
For severe pneumonia patients with chest tightness or difficulty breathing, oxygen therapy is required to alleviate symptoms. Common methods include nasal cannula oxygen, mask oxygen, non-invasive ventilation, and invasive ventilation[3]. -
Medication
- For mild adenovirus infections, symptomatic treatment is used. Cough suppressants like dextromethorphan may be prescribed, while eye infections can be treated with ribavirin eye drops[6-8].
- For severe cases, antiviral drugs such as ribavirin, vidarabine, cidofovir, or interferon-α may be administered, though they may cause side effects like anemia, fatigue, nausea, or kidney dysfunction. Patients should maintain ventilation, exercise, and improve immunity during treatment[4].
- Immunocompromised patients may receive thymosin or immunoglobulin to enhance immunity[4].
Can adenovirus infection be completely cured?
With timely and standardized treatment, adenovirus infection can be fully cured, though recovery may take longer. Patients should rest, exercise moderately, and maintain good health to shorten treatment duration[6-8].
Is hospitalization necessary for adenovirus infection?
Children with adenovirus infection are generally advised to be hospitalized, as adenovirus pneumonia can be severe and requires active treatment. Since there is no specific antiviral drug, supportive care (e.g., fever reduction, cough relief) is essential, and home treatment may delay recovery.
Infants with adenovirus infection require hospitalization, especially if gastrointestinal involvement risks intussusception—a serious condition needing close monitoring.
Adults may choose outpatient or inpatient care based on symptom severity[6-8].
How long does it take to recover from adenovirus infection?
Adenovirus infection typically takes about 14 days to heal, while severe cases may require 3–4 weeks[6-8].
Patients should adhere to medication or intravenous therapy. Since no specific antiviral exists, broad-spectrum antivirals combined with symptomatic treatment are used. Oral medication may be continued post-recovery to consolidate results[6-8].
How should pregnant women with adenovirus infection be treated?
If a pregnant woman has no obvious symptoms or organ dysfunction, medical treatment may not be necessary, as adenovirus is self-limiting and lacks targeted antivirals. Long-term medication should be avoided to prevent fetal harm.
However, if severe symptoms or organ dysfunction occur, symptom-relief drugs (under medical guidance) may be used, though antivirals are still discouraged. Ventilation and mild exercise can aid recovery[7,8].
How often should follow-up checks be done after adenovirus infection?
Follow-up is recommended only after symptoms fully resolve, usually in 1–2 weeks (or a month for severe cases).
The purpose is to check for residual adenovirus. If detected, extended treatment may be needed to prevent relapse[7].
DIET & LIFESTYLE
What dietary precautions should adenovirus-infected individuals take?
Adenovirus-infected individuals should pay attention to dietary hygiene, wash and disinfect hands before eating, and thoroughly clean food.
Avoid foods high in fat, especially for patients with digestive tract infections, as their digestive function may be weaker. Easily digestible foods like porridge or soft noodles are recommended.
Additionally, avoid overeating, consuming spicy or irritating foods, and abstain from smoking and alcohol. These poor dietary habits can increase bodily burden, disrupt metabolic secretions, and hinder recovery[7,8].
What lifestyle precautions should adenovirus-infected individuals take?
- Adenovirus-infected individuals should rest adequately, ensure proper ventilation, stay warm, and drink plenty of water.
- After symptoms improve, light exercise is acceptable, but avoid overexertion.
- Maintain a positive mindset, as adenovirus infection is not a severe illness and excessive worry is unnecessary.
- Follow medical advice and take prescribed medications on time for effective treatment[7,8].
Can adenovirus-infected patients rely on dietary therapy?
Dietary therapy is generally not recommended for adenovirus-infected patients. Although adenovirus is self-limiting and may resolve on its own, patients with clinical symptoms risk worsening their condition if not treated promptly. Untreated adenovirus infections may lead to other health complications.
Currently, there is no specific medication for adenovirus, and dietary therapy cannot eliminate the virus. However, maintaining dietary hygiene and eating light meals can aid recovery[7,8].
Can adenovirus-infected patients work or study during illness?
Patients may engage in light work or study according to their condition, but should avoid overexertion.
Generally, adenovirus infection causes symptoms like fever, chills, headaches, and may lead to pneumonia, gastroenteritis, or conjunctivitis, affecting daily life. Rest is advised, and patients should avoid staying up late or excessive fatigue to facilitate recovery[7,8].
PREVENTION
How to prevent adenovirus infection?
- Adenovirus can spread through droplets, fecal-oral transmission, and contact. Therefore, it is necessary to wash hands frequently, ventilate rooms, and disinfect items promptly in daily life.
- If there are adenovirus-infected patients or asymptomatic carriers around, avoid direct contact with their excretions, secretions, or other contaminated items to prevent the virus from entering the body through the mouth, nose, or eye mucosa via hands.
- At the same time, drink plenty of water, consume fresh fruits and vegetables, and exercise regularly.
- Adenovirus infections often occur in winter and spring. During these seasons, keep warm and avoid crowded public places. Wear a mask when going out[7].
How to avoid transmitting adenovirus to others after infection?
- Those with mild symptoms should rest at home in isolation and minimize outings. If severe symptoms such as persistent high fever, palpitations, or shortness of breath occur, seek medical attention promptly and cooperate with treatment.
- Avoid public places. Wear a mask when going out and maintain distance from others.
- Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, keep a safe distance from others, and avoid contaminating the surrounding air, objects, or infecting others.
- Avoid sharing cups, utensils, or other personal items with others[2,4].
Can adenovirus infection recur?
Recurrence is possible after recovering from adenovirus infection.
Therefore, even after recovery, patients should maintain good living and dietary habits, avoid exposure to cold, ventilate rooms, wash hands frequently, disinfect regularly, exercise consistently, and boost immunity to prevent reinfection[7].
Can adenovirus infection be prevented through vaccination?
China has not yet fully developed a vaccine to prevent adenovirus infection, but significant progress has been made in research on type 3 and type 7 adenovirus vaccines[10].